Introduction of css
Css(cascading style sheet)
|
Table of contents css syntax Types of css 1.Internal css 2.External Css 3.Inline css |
CSS describes how HTML elements should be displayed.
This tutorial will teach you CSS from basic to advanced.
A CSS rule consists of a selector and a declaration block.
CSS Syntax
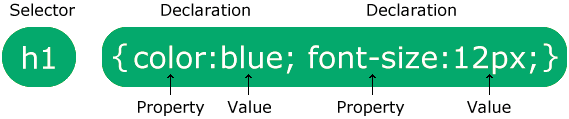
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
Example
p {
color: red;
text-align: center; Background-color:white;
}
p is a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).color is a property, and red is the property valuetext-align is a property, and center is the property value
Program
<style>p { color: red; text-align: center;} </style></head><body>
<p>Hello World!</p><p>These paragraphs are styled with CSS.</p>
</body>
OutputHello World!
These paragraphs are styled with CSS.
Types of css
There are 3types of css cascanding style sheet there as follows-
1 internal css
2 external css
3 inline css
1 Internal css
Internal CSS is specified at the beginning of an HTML document.
Example-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: linen;
}
h1 {
color: maroon;
margin-left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
2 External css
External CSS is a file that HTML files will link to other.
Example-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension
Here is how the "mystyle.css" file looks:
"mystyle.css"
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: navy;
margin-left: 20px;
}
3 Inline css
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
Inline CSS is written for a specific element in the HTML document.
Example -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is a heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
 |
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style. |
Example
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
pis a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).coloris a property, andredis the property valuetext-alignis a property, andcenteris the property value
Hello World!
These paragraphs are styled with CSS.
Types of css
There are 3types of css cascanding style sheet there as follows-
1 internal css
2 external css
3 inline css
1 Internal css
Internal CSS is specified at the beginning of an HTML document.
Example-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: linen;
}
h1 {
color: maroon;
margin-left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>2 External css
External CSS is a file that HTML files will link to other.
Example-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension
Here is how the "mystyle.css" file looks:
"mystyle.css"
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: navy;
margin-left: 20px;
}3 Inline css
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
Inline CSS is written for a specific element in the HTML document.
Example -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is a heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>


EmoticonEmoticon
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.